memblock算法是linux内核初始化阶段的一个内存分配器(它取代了原来的bootmem算法),实现较为简单。负责page allocator初始化之前的内存管理和分配请求。
分析memblock算法,可以从几点入手:
- memblock算法初始化;
- memblock算法管理内存的申请和释放;
memblock算法前的准备:
前面已经分析了linux系统在初始化的过程中,使用int 15中断探知了机器的内存分布图(e820图),其数据是存储在boot_params.e820_map里面,这里面是没有经过整理的数据,杂乱无章,毕竟BIOS没有责任做整理内存的事情,所以这部分事情由系统来实现。那么看一下linux如何实现这部分功能的,这部分功能是在setup_memory_map()里面实现的。
该函数在初始化中的调用位置:
start_kernel()
└->setup_arch()
└->setup_memory_map();
函数实现:
【file:/arch/x86/kernel/e820.c】
void __init setup_memory_map(void)
{
char *who;
who = x86_init.resources.memory_setup();
memcpy(&e820_saved, &e820, sizeof(struct e820map));
printk(KERN_INFO "e820: BIOS-provided physical RAM map:\n");
e820_print_map(who);
}
可以看到实现很简单,先是调用了一个钩子函数,然后将e820保存到e820_saved里面,再往下就是print函数。很明显可以看到关键点在于这个钩子函数的实现,在x86_init.c里面可以找到x86_init该结构体变量的定义:
【file:/arch/x86/kernel/x86_init.c】
/*
* The platform setup functions are preset with the default functions
* for standard PC hardware.
*/
struct x86_init_ops x86_init __initdata = {
.resources = {
.probe_roms = probe_roms,
.reserve_resources = reserve_standard_io_resources,
.memory_setup = default_machine_specific_memory_setup,
},
.mpparse = {
.mpc_record = x86_init_uint_noop,
.setup_ioapic_ids = x86_init_noop,
.mpc_apic_id = default_mpc_apic_id,
.smp_read_mpc_oem = default_smp_read_mpc_oem,
.mpc_oem_bus_info = default_mpc_oem_bus_info,
.find_smp_config = default_find_smp_config,
.get_smp_config = default_get_smp_config,
},
.irqs = {
.pre_vector_init = init_ISA_irqs,
.intr_init = native_init_IRQ,
.trap_init = x86_init_noop,
},
.oem = {
.arch_setup = x86_init_noop,
.banner = default_banner,
},
.paging = {
.pagetable_init = native_pagetable_init,
},
.timers = {
.setup_percpu_clockev = setup_boot_APIC_clock,
.tsc_pre_init = x86_init_noop,
.timer_init = hpet_time_init,
.wallclock_init = x86_init_noop,
},
.iommu = {
.iommu_init = iommu_init_noop,
},
.pci = {
.init = x86_default_pci_init,
.init_irq = x86_default_pci_init_irq,
.fixup_irqs = x86_default_pci_fixup_irqs,
},
};
由此可以看到该钩子函数挂的是default_machine_specific_memory_setup()。
进一步看一下该函数的实现:
【file:/arch/x86/kernel/e820.c】
char *__init default_machine_specific_memory_setup(void)
{
char *who = "BIOS-e820";
u32 new_nr;
/*
* Try to copy the BIOS-supplied E820-map.
*
* Otherwise fake a memory map; one section from 0k->640k,
* the next section from 1mb->appropriate_mem_k
*/
new_nr = boot_params.e820_entries;
sanitize_e820_map(boot_params.e820_map,
ARRAY_SIZE(boot_params.e820_map),
&new_nr);
boot_params.e820_entries = new_nr;
if (append_e820_map(boot_params.e820_map, boot_params.e820_entries)
< 0) {
u64 mem_size;
/* compare results from other methods and take the greater */
if (boot_params.alt_mem_k
< boot_params.screen_info.ext_mem_k) {
mem_size = boot_params.screen_info.ext_mem_k;
who = "BIOS-88";
} else {
mem_size = boot_params.alt_mem_k;
who = "BIOS-e801";
}
e820.nr_map = 0;
e820_add_region(0, LOWMEMSIZE(), E820_RAM);
e820_add_region(HIGH_MEMORY, mem_size << 10, E820_RAM);
}
/* In case someone cares... */
return who;
}
在这个函数里面,可以看到前面探测到的内存布局信息boot_params.e820_map在这里被使用了。
首先分析一下sanitize_e820_map(),该函数把e820信息进行了如何处理,函数实现:
【file:/arch/x86/kernel/e820.c】
int __init sanitize_e820_map(struct e820entry *biosmap, int max_nr_map,
u32 *pnr_map)
{
static struct change_member change_point_list[2*E820_X_MAX] __initdata;
static struct change_member *change_point[2*E820_X_MAX] __initdata;
static struct e820entry *overlap_list[E820_X_MAX] __initdata;
static struct e820entry new_bios[E820_X_MAX] __initdata;
unsigned long current_type, last_type;
unsigned long long last_addr;
int chgidx;
int overlap_entries;
int new_bios_entry;
int old_nr, new_nr, chg_nr;
int i;
/* if there's only one memory region, don't bother */
if (*pnr_map < 2)
return -1;
old_nr = *pnr_map;
BUG_ON(old_nr > max_nr_map);
/* bail out if we find any unreasonable addresses in bios map */
for (i = 0; i < old_nr; i++)
if (biosmap[i].addr + biosmap[i].size < biosmap[i].addr)
return -1;
/* create pointers for initial change-point information (for sorting) */
for (i = 0; i < 2 * old_nr; i++)
change_point[i] = &change_point_list[i];
/* record all known change-points (starting and ending addresses),
omitting those that are for empty memory regions */
chgidx = 0;
for (i = 0; i < old_nr; i++) {
if (biosmap[i].size != 0) {
change_point[chgidx]->addr = biosmap[i].addr;
change_point[chgidx++]->pbios = &biosmap[i];
change_point[chgidx]->addr = biosmap[i].addr +
biosmap[i].size;
change_point[chgidx++]->pbios = &biosmap[i];
}
}
chg_nr = chgidx;
/* sort change-point list by memory addresses (low -> high) */
sort(change_point, chg_nr, sizeof *change_point, cpcompare, NULL);
/* create a new bios memory map, removing overlaps */
overlap_entries = 0; /* number of entries in the overlap table */
new_bios_entry = 0; /* index for creating new bios map entries */
last_type = 0; /* start with undefined memory type */
last_addr = 0; /* start with 0 as last starting address */
/* loop through change-points, determining affect on the new bios map */
for (chgidx = 0; chgidx < chg_nr; chgidx++) {
/* keep track of all overlapping bios entries */
if (change_point[chgidx]->addr ==
change_point[chgidx]->pbios->addr) {
/*
* add map entry to overlap list (> 1 entry
* implies an overlap)
*/
overlap_list[overlap_entries++] =
change_point[chgidx]->pbios;
} else {
/*
* remove entry from list (order independent,
* so swap with last)
*/
for (i = 0; i < overlap_entries; i++) {
if (overlap_list[i] ==
change_point[chgidx]->pbios)
overlap_list[i] =
overlap_list[overlap_entries-1];
}
overlap_entries--;
}
/*
* if there are overlapping entries, decide which
* "type" to use (larger value takes precedence --
* 1=usable, 2,3,4,4+=unusable)
*/
current_type = 0;
for (i = 0; i < overlap_entries; i++)
if (overlap_list[i]->type > current_type)
current_type = overlap_list[i]->type;
/*
* continue building up new bios map based on this
* information
*/
if (current_type != last_type) {
if (last_type != 0) {
new_bios[new_bios_entry].size =
change_point[chgidx]->addr - last_addr;
/*
* move forward only if the new size
* was non-zero
*/
if (new_bios[new_bios_entry].size != 0)
/*
* no more space left for new
* bios entries ?
*/
if (++new_bios_entry >= max_nr_map)
break;
}
if (current_type != 0) {
new_bios[new_bios_entry].addr =
change_point[chgidx]->addr;
new_bios[new_bios_entry].type = current_type;
last_addr = change_point[chgidx]->addr;
}
last_type = current_type;
}
}
/* retain count for new bios entries */
new_nr = new_bios_entry;
/* copy new bios mapping into original location */
memcpy(biosmap, new_bios, new_nr * sizeof(struct e820entry));
*pnr_map = new_nr;
return 0;
}
第一个for循环:
/* bail out if we find any unreasonable addresses in bios map */
for (i = 0; i < old_nr; i++)
if (biosmap[i].addr + biosmap[i].size < biosmap[i].addr)
return -1;
这里是将e820做一个全面检测,检测是否存在不合理的内存布局信息项,存在不合理项则直接退出。
第二个for循环:
/* create pointers for initial change-point information (for sorting) */
for (i = 0; i < 2 * old_nr; i++)
change_point[i] = &change_point_list[i];
将change_point和change_point_list关联起来,实际上change_point_list只是占用一个栈空间而已,真正起到作用的是change_point。
第三个for循环和sort函数的调用一起来分析:
/* record all known change-points (starting and ending addresses),
omitting those that are for empty memory regions */
chgidx = 0;
for (i = 0; i < old_nr; i++) {
if (biosmap[i].size != 0) {
change_point[chgidx]->addr = biosmap[i].addr;
change_point[chgidx++]->pbios = &biosmap[i];
change_point[chgidx]->addr = biosmap[i].addr +
biosmap[i].size;
change_point[chgidx++]->pbios = &biosmap[i];
}
}
chg_nr = chgidx;
/* sort change-point list by memory addresses (low -> high) */
sort(change_point, chg_nr, sizeof *change_point, cpcompare, NULL);
这里是把change_point初始化并与boot_params.e820_map各项的起始地址和结束地址分别关联起来,继而通过sort来进行排序。排序的结果就是将各项内存布局信息所标示的内存空间起始地址和结束地址由低往高进行排序。如果两者地址值相等,则以两者的e820_map项信息所标示的内存空间尾做排序依据,哪个空间尾更后,则该项排在等值项后面。
看一下最后的for循环:
/* loop through change-points, determining affect on the new bios map */
for (chgidx = 0; chgidx < chg_nr; chgidx++) {
/* keep track of all overlapping bios entries */
if (change_point[chgidx]->addr ==
change_point[chgidx]->pbios->addr) {
/*
* add map entry to overlap list (> 1 entry
* implies an overlap)
*/
overlap_list[overlap_entries++] =
change_point[chgidx]->pbios;
} else {
/*
* remove entry from list (order independent,
* so swap with last)
*/
for (i = 0; i < overlap_entries; i++) {
if (overlap_list[i] ==
change_point[chgidx]->pbios)
overlap_list[i] =
overlap_list[overlap_entries-1];
}
overlap_entries–;
}
/*
* if there are overlapping entries, decide which
* “type” to use (larger value takes precedence —
* 1=usable, 2,3,4,4+=unusable)
*/
current_type = 0;
for (i = 0; i < overlap_entries; i++)
if (overlap_list[i]->type > current_type)
current_type = overlap_list[i]->type;
/*
* continue building up new bios map based on this
* information
*/
if (current_type != last_type) {
if (last_type != 0) {
new_bios[new_bios_entry].size =
change_point[chgidx]->addr – last_addr;
/*
* move forward only if the new size
* was non-zero
*/
if (new_bios[new_bios_entry].size != 0)
/*
* no more space left for new
* bios entries ?
*/
if (++new_bios_entry >= max_nr_map)
break;
}
if (current_type != 0) {
new_bios[new_bios_entry].addr =
change_point[chgidx]->addr;
new_bios[new_bios_entry].type = current_type;
last_addr = change_point[chgidx]->addr;
}
last_type = current_type;
}
}
这个循环里面干了什么事情呢?其大概作用就是把已经排序完了的change_point做整合,将重叠的内存空间根据属性进行筛选,并将同属性的相邻内存空间进行合并处理。具体实现流程为:
- 最初第一次循环加入change_point项,将根据当前change_point记录的地址项是否与其关联的e820_map项的起始地址一致,如果一致(第一次必然是一致的),表示当前项是某内存块的起始地址,将其加入到overlap_list中去,然后该项将会添加到new_bios中并更新last_addr,最后更新当前内存块的内存类型到last_type中(这个类型当做优先级理解,会容易理解代码的,0优先级最低);
- 第二次循环加入change_point项,就会开始遇到各种状况了:
- 假设change_point新加入项是第一项的内存尾,那么overlap_list将会移除该项,new_bios将会更新当前项的内存块大小,只要内存块大小不为0,那么new_bios_entry自加,new_bios开始新一项的内容记录;
- 假设change_point新加入项是新的内存块地址头,那么overlap_list将会新增一项,然后current_type将会更新到overlap_list列表中的所有项的类型最大值(最高优先级),接下来又出现新状况了:
- 如果当前新加入change_point的类型值等于前者,继续开始下一循环;
- 如果当前新加入change_point的类型值大于前者,那么new_bios将会以该change_point项纪录的地址作为new_bios前一项的结束地址,然后更新大小到new_bios中,开启new_bios的新一项的记录;
- 如果当前新加入change_point的类型值小于前者,由于current_type将会仍然保持前者的类型值,后续将会跳过开始下一循环;
- 第三次循环加入change_point项,基于前面第二次循环加入change_point项的情况,如果是情况A,那么问题很简单,就是一个新开始而已;如果是情况B,将会出现稍微复杂的情况:
- 假设该change_point新加入项又是新的内存块头,将会涉及类型值不同的问题,其实也就是重复前面类型第二次循环的情况B的场景,这里就不细述了;
- 假设该change_point新加入项是前面的内存块尾,那么可能的状况是:
- 如果前面已加入的两项类型相同,即B.a的情形,当前作为内存尾新加入change_point的类型值必然也是相同的,这仅会把与overlap_list中配对的那一项从队列中删除,继续开始加入change_point下一项;
- 如果前面两项,第一项类型值大于第二项,即B.c的情形,若当前项作为第一项的尾加入,那么当前的new_bios项将会以此作为结尾;但是若当前项作为第二项的尾加入,那么将把第二项从overlap_list中删除;
- 如果前面两项,第二项类型值大于第一项,即B.b的情形,若当前项作为第一项的尾加入,也仅是将第一项从overlap_list中删除;若当前项作为第一项的尾加入,那么new_bios将会就此作为尾完成当前项;
后续的循环加入change_point项也仅是前面的场景演变而已,这里不细述了。那么从前面的信息来看,这个函数的目的是什么基本明了,也就是将boot_params.e820_map里面的内存布局根据顺序和重叠情况,将连续的同类型的内存块合并,将不同类型的内存块根据高低优先级进行内存块划分拆开。
正如下描述的一样:
【file:/arch/x86/kernel/e820.c】 /* * Sanitize the BIOS e820 map. * * Some e820 responses include overlapping entries. The following * replaces the original e820 map with a new one, removing overlaps, * and resolving conflicting memory types in favor of highest * numbered type. * * The input parameter biosmap points to an array of 'struct * e820entry' which on entry has elements in the range [0, *pnr_map) * valid, and which has space for up to max_nr_map entries. * On return, the resulting sanitized e820 map entries will be in * overwritten in the same location, starting at biosmap. * * The integer pointed to by pnr_map must be valid on entry (the * current number of valid entries located at biosmap) and will * be updated on return, with the new number of valid entries * (something no more than max_nr_map.) * * The return value from sanitize_e820_map() is zero if it * successfully 'sanitized' the map entries passed in, and is -1 * if it did nothing, which can happen if either of (1) it was * only passed one map entry, or (2) any of the input map entries * were invalid (start + size < start, meaning that the size was * so big the described memory range wrapped around through zero.) * * Visually we're performing the following * (1,2,3,4 = memory types)... * * Sample memory map (w/overlaps): * ____22__________________ * ______________________4_ * ____1111________________ * _44_____________________ * 11111111________________ * ____________________33__ * ___________44___________ * __________33333_________ * ______________22________ * ___________________2222_ * _________111111111______ * _____________________11_ * _________________4______ * * Sanitized equivalent (no overlap): * 1_______________________ * _44_____________________ * ___1____________________ * ____22__________________ * ______11________________ * _________1______________ * __________3_____________ * ___________44___________ * _____________33_________ * _______________2________ * ________________1_______ * _________________4______ * ___________________2____ * ____________________33__ * ______________________4_ */
为了方便理解,整理出一张草图:
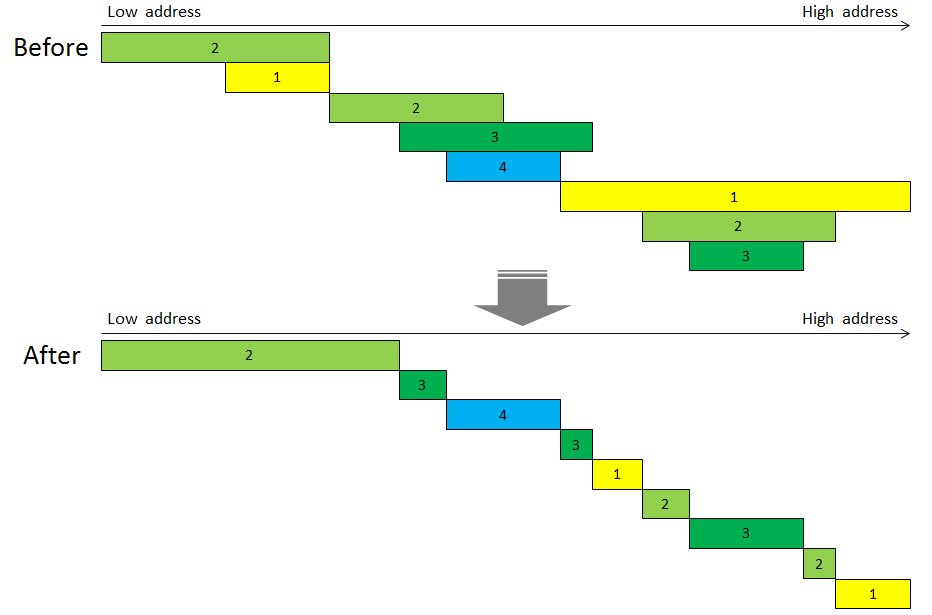
连续的同类型的合并到一块里面,不同类型的各自为政,不同类型重叠部分根据类型优先级高低拆分,依高优先级顺序保证各类型的内存块的完整性。额外废话一句:目前玩虚拟机没有遇到过上面这么复杂的情况,但是不能否认这段代码是设计来干这活的。
从sanitize_e820_map出来后,回到default_machine_specific_memory_setup()中,接下来是append_e820_map的函数:
【file:/arch/x86/kernel/e820.c】
static int __init append_e820_map(struct e820entry *biosmap, int nr_map)
{
/* Only one memory region (or negative)? Ignore it */
if (nr_map < 2)
return -1;
return __append_e820_map(biosmap, nr_map);
}
append_e820_map()封装调用__append_e820_map():
【file:/arch/x86/kernel/e820.c】
static int __init __append_e820_map(struct e820entry *biosmap, int nr_map)
{
while (nr_map) {
u64 start = biosmap->addr;
u64 size = biosmap->size;
u64 end = start + size;
u32 type = biosmap->type;
/* Overflow in 64 bits? Ignore the memory map. */
if (start > end)
return -1;
e820_add_region(start, size, type);
biosmap++;
nr_map--;
}
return 0;
}
循环调用e820_add_region()将整理后的boot_params.e820_map做添加操作:
【file:/arch/x86/kernel/e820.c】
void __init e820_add_region(u64 start, u64 size, int type)
{
__e820_add_region(&e820, start, size, type);
}
e820_add_region()封装__e820_add_region():
【file:/arch/x86/kernel/e820.c】
static void __init __e820_add_region(struct e820map *e820x, u64 start, u64 size,
int type)
{
int x = e820x->nr_map;
if (x >= ARRAY_SIZE(e820x->map)) {
printk(KERN_ERR "e820: too many entries; ignoring [mem %#010llx-%#010llx]\n",
(unsigned long long) start,
(unsigned long long) (start + size - 1));
return;
}
e820x->map[x].addr = start;
e820x->map[x].size = size;
e820x->map[x].type = type;
e820x->nr_map++;
}
而__e820_add_region()则是将各项信息往e820做添加操作。说白了,就是将boot_params.e820_map转入到e820图中。
最后顺便看一下e820_print_map()函数的实现:
【file:/arch/x86/kernel/e820.c】
void __init e820_print_map(char *who)
{
int i;
for (i = 0; i < e820.nr_map; i++) {
printk(KERN_INFO "%s: [mem %#018Lx-%#018Lx] ", who,
(unsigned long long) e820.map[i].addr,
(unsigned long long)
(e820.map[i].addr + e820.map[i].size - 1));
e820_print_type(e820.map[i].type);
printk(KERN_CONT "\n");
}
}
它是将钩子函数返回的内容打印出来,打印出来的内容可以在shell上面通过dmesg命令查看得到,例如:
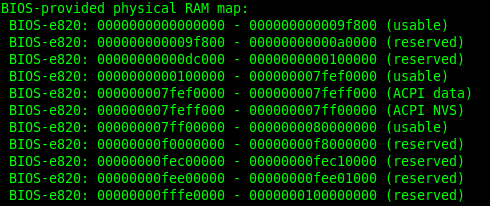
最后总结一下,以上代码干了这么多活,主要就是为了把通过BIOS中断探测到的内存布局信息boot_params.e820_map做整合处理,完了转存到变量e820中。
